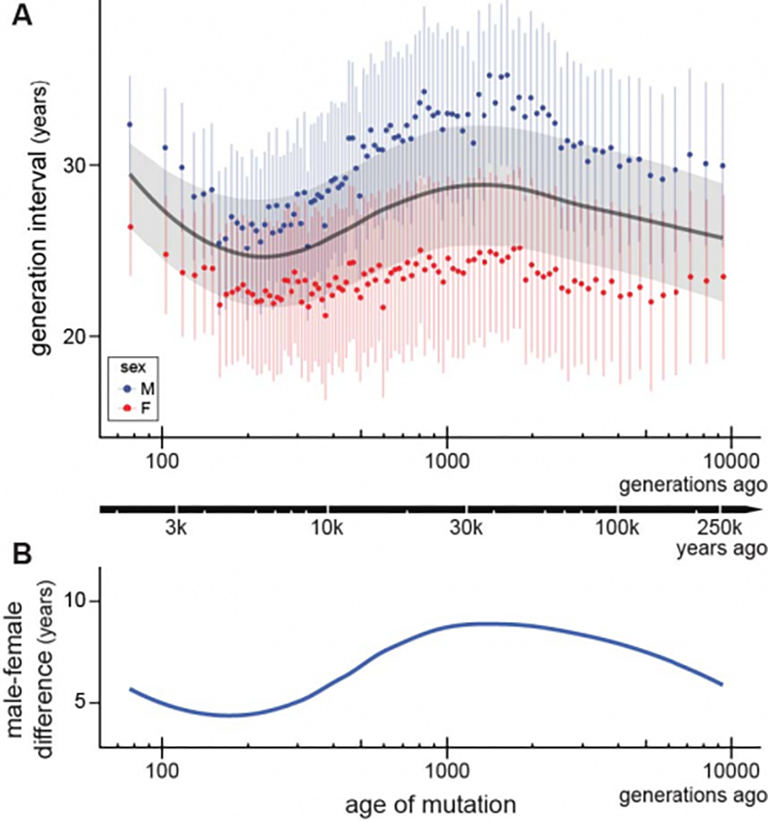
Evolutionary biologists at IU found that fathers are consistently older than mothers throughout human evolutionary history, but that age gap has shrunk.
The length of a specific generation can tell us a lot about the biology and social organization of humans. Now, researchers at Indiana University can determine the average age that women and men had children throughout human evolutionary history with a new method they developed using DNA mutations.
The researchers said this work can help us understand the environmental challenges experienced by our ancestors and may also help us in predicting the effects of future environmental change on human societies.
“Through our research on modern humans, we noticed that we could predict the age at which people had children from the types of DNA mutations they left to their children,” said study co-author Matthew Hahn, Distinguished Professor of biology in the College of Arts and Sciences and of computer science in the Luddy School of Informatics, Computing, and Engineering at IU Bloomington. “We then applied this model to our human ancestors to determine what age our ancestors procreated.”
According to the study, published today in Science Advances and co-authored by IU postdoctoral researcher Richard Wang, the average age that humans had children throughout the past 250,000 years is 26.9. Furthermore, fathers were consistently older, at 30.7 years on average, than mothers, at 23.2 years on average, but the age gap has shrunk in the past 5,000 years, with the study’s most recent estimates of maternal age averaging 26.4 years. The shrinking gap seems to largely be due to mothers having children at older ages.


 The College of Arts
The College of Arts