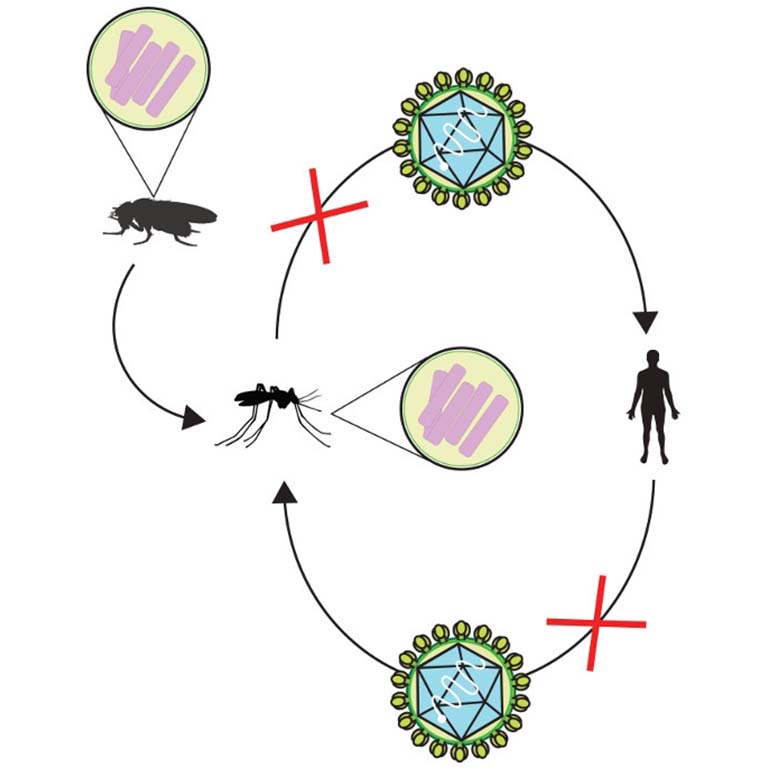
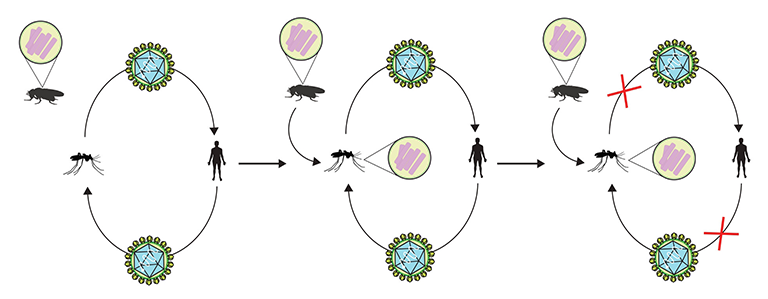
A new study from Indiana University may explain how a bacterium called Wolbachia prevents mosquitoes from transmitting deadly diseases such as dengue fever, West Nile virus and Zika.
Published today in the journal PLOS Pathogens, the study is one of the first to identify a specific biological mechanism that prevents mosquitoes infected with this bacterium from transmitting diseases to humans. It could also potentially open a path toward methods to block disease transmission without Wolbachia, an organism whose long-term effect on the environment is unknown.



 The College of Arts
The College of Arts